What is the Novel Corona Virus?
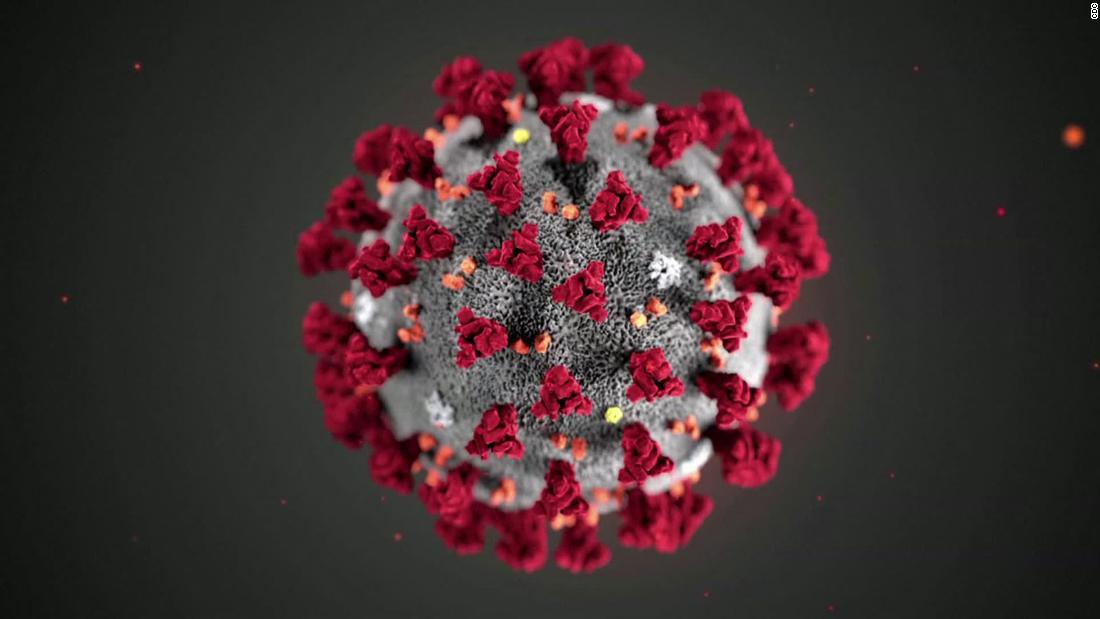
SARS-CoV-2
Coronaviruses (CoV) are a large family of viruses that cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases. A novel coronavirus (nCoV) is a new strain that has not been previously identified in humans.
3D model of the novel coronavirus
The infamous spikes
Coronavirus entry into host cells is mediated by the transmembrane spike (S) glycoprotein that forms homotrimers protruding from the viral surface.S comprises two functional subunits responsible for binding to the host cell receptor.